Page 111 - ingenioren
P. 111
Technical Reference
How Filter Media Functions In a Filtration How Filter Media Collects Particles
System
Basic ways filter media captures particles
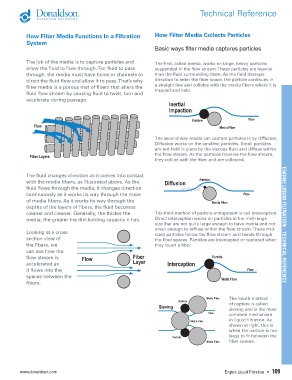
The job of the media is to capture particles and The first, called inertia, works on large, heavy particles
allow the fluid to flow through. For fluid to pass suspended in the flow stream. These particles are heavier
through, the media must have holes or channels to than the fluid surrounding them. As the fluid changes
direct the fluid flow and allow it to pass. That’s why direction to enter the fiber space, the particle continues in
filter media is a porous mat of fibers that alters the a straight line and collides with the media fibers where it is
trapped and held.
fluid flow stream by causing fluid to twist, turn and
accelerate during passage.
The second way media can capture particles is by diffusion.
Diffusion works on the smallest particles. Small particles
are not held in place by the viscous fluid and diffuse within
the flow stream. As the particles traverse the flow stream,
they collide with the fiber and are collected.
The fluid changes direction as it comes into contact
with the media fibers, as illustrated above. As the
fluid flows through the media, it changes direction
continuously as it works its way through the maze
of media fibers. As it works its way through the
depths of the layers of fibers, the fluid becomes
cleaner and cleaner. Generally, the thicker the The third method of particle entrapment is call interception.
media, the greater the dirt-holding capacity it has. Direct interception works on particles in the mid-range
size that are not quite large enough to have inertia and not ENGINE LIQUID FILTRATION - TECHNICAL REFERENCE
small enough to diffuse within the flow stream. These mid-
Looking at a cross sized particles follow the flow stream as it bends through
section view of the fiber spaces. Particles are intercepted or captured when
the fibers, we they touch a fiber.
can see how the
flow stream is
accelerated as
it flows into the
spaces between the
fibers.
The fourth method
of capture is called
sieving and is the most
common mechanism
in liquid filtration. As
shown at right, this is
when the particle is too
large to fit between the
fiber spaces.
www.donaldson.com Engine Liquid Filtration • 109